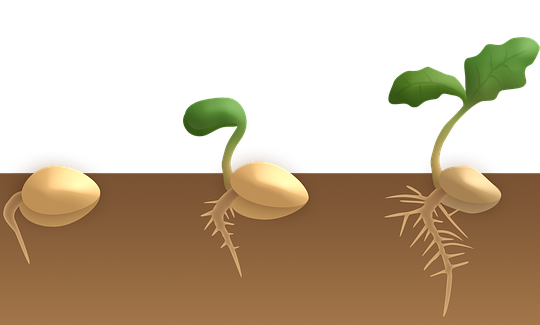
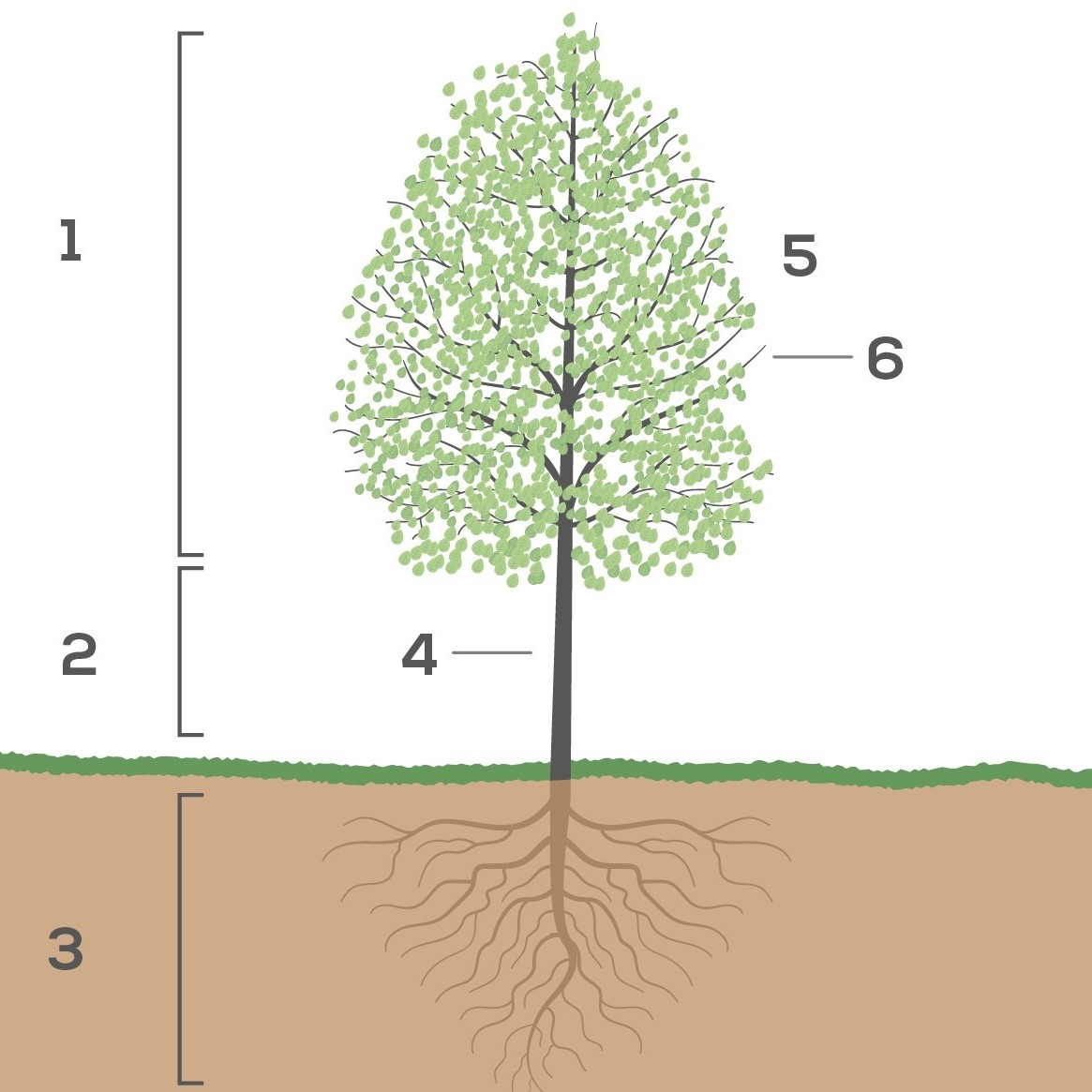
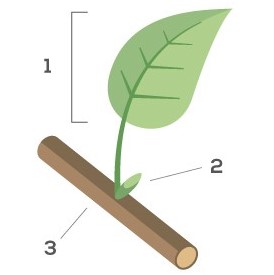
Are you interested in better knowing trees and the forest? Discover the technical vocabulary, lexicon and definitions of tree-related terms and enrich your knowledge of the forest, of tree species, of the anatomy of trees, of wood and soil types!
The trees are grouped into two large groups: deciduous on one side and conifers or conifers on the other. Conifers usually have leaves reduced to needles ( pine , spruce ) or scales ( thuya ). Their foliage is persistent, except in some such as larch. The photosynthesis of conifers continues partially, giving them faster growth than those of hardwoods. Thus, conifers reach higher sizes faster. From an ecological point of view, softwoods are generally less demanding with regard to the composition of the soil than hardwoods and also more resistant to cold.